Given
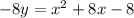
Solving for y,
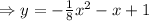
Therefore, since the coefficient that accompanies the x^2 is negative, the parabola opens downwards.
In general, the vertex and general form of a parabola are
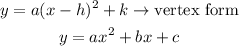
Where (h,k) is the vertex of the parabola
Then,
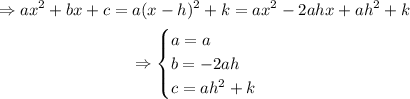
Finding h and k in our case,
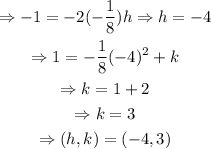
The vertex of the parabola is (-4,3)
Notice that the parabola opens downwards and it is parallel to the y-axis; therefore,
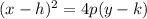
Where (h,k) is the vertex. In our case, from the vertex form of the quadratic equation,
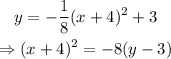
Thus,
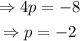
The distance from the focus to the vertex is 2.
Because the graph of the function opens downwards, we can find its focus as shown below,
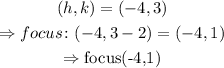
The focus is (-4,1)
Because the graph opens downward and p=-2, the equation of the directrix is
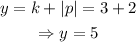
The directrix is y=5
Finally, the axis of symmetry is a line perpendicular to the directrix and crosses the vertex; therefore,
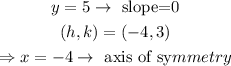
The axis of symmetry is x=-4