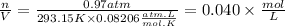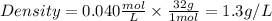Density is defined as mass divided by volume. To find these parameters we will use the ideal gas equation that tells us:
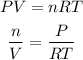
where,
n is the moles of the gas
V is the volume
P is the pressure of the gas
T is the temperature
R is a constant = 0.08206 (atm.L)/(mol.K)
We see that we will have the molar density of oxygen as a result, to obtain the density we use the molar mass of oxygen, so we will have:
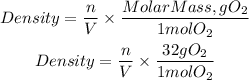
Now let's substitute the data we get:
1)TPN conditions are equal to
T=20°C=293.15K
P=1atm
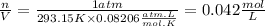
Density will be:
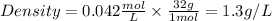
2) T=20°C=293.15K
P=760mmHg=0.97atm