We know that the sum of n terms of a series is:
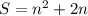
We have to find the 3 first terms of the series.
The first term will be equal to the sum of all the terms when n = 1, as it is the only term present. Then:
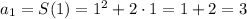
We can calculate the second term (a2) as:
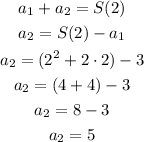
Finally, the third term will be:
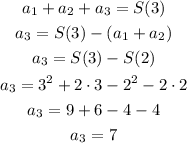
NOTE: we can calculate any term (an) as:
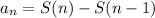
Answer: the first 3 terms are a1 = 3, a2 = 5 and a3 = 7.