Given
Suppose a monochromatic light incident on a single slit produces a diffraction
pattern.
To find
(a) How would the pattern differ if you decrease the wavelength of the light by
half?
(b) How would the pattern differ if you tripled both the wavelength and slit width
at the same time?
Step-by-step explanation
The fringe width is given by
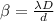
where D is the distance between the slit and the screen, d is the width of the slit.
a. If the wavelength is decreased by half then the fringe width decreases by half. So teh distance between the consecutive bright spot of dark spot is reduced to half.
b. When the wavelength and the slit width would be tripled then the fringe width is
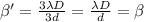
Thus the fringe width remains same. So the diffraction patternn remains same.