ANSWER
d. none of the above
Step-by-step explanation
The Law of Universal Gravitation states that:
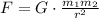
Where F is the force and r is the distance. Note that the force varies inversely with the square of the distance.
This means that the graph is definitely not linear, because the equation should have the form:
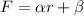
where alpha and beta are constants.
It is not parabolic either, because in that case the form would be:
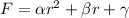
Again, alpha, beta and gamma are constants.
And it's not circular, because we should have the square of the force too.
This said, the answer is none of the above.
Note: the graph is hiperbolic.