Step-by-step explanation:
To find the speed of the cue ball after the collision, we will use the conservation of the horizontal momentum, so we can write the following equation
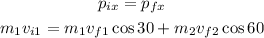
Where m1 is the mass of the cue ball, m2 is the mass of the other ball, vi1 is the initial velocity of the cue ball, vf1 is the final velocity of the cue ball, and vf2 is the final velocity of the other ball.
So
Replacing m1 = 0.17 kg, m2 = 0.17 kg, vi1 = 3.8 m.
