The vertices of a triangle ABC are given as
A(6, 6), B(6, -6), C(0, 0)
A sequence of transformations was applied to triangle ABC which resulted in the triangle A'B'C' as shown in the given figure.
Let us first draw the original triangle ABC to better understand the problem
From the given figure, we see that the coordinates of the triangle A'B'C' are
A'(-2, 2), B'(2, 2), C'(0, 0)
Recall that the rule for a 90° counter-clockwise rotation is given by
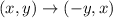
Let us apply the above transformation to the pre-image that is triangle ABC
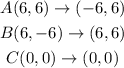
Now let us apply a dilation by a scale factor of 1/3 about the origin
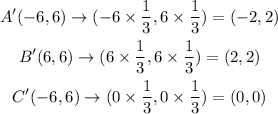
As you can see, we have got the same coordinates as the given
Therefore, the sequence of transformations is
A 90° counter-clockwise rotation about the origin, then, a dilation by a scale factor of 1/3 with a center of dilation at the origin.
So, the 1st option is the correct answer.