ANSWER
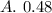
Step-by-step explanation
We want to solve for x in the equation:
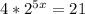
First, divide both sides of the equation by 4:
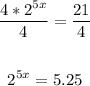
Find the logarithm of both sides of the equation:
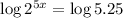
Simplify the left-hand side of the equation:
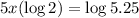
Divide both sides by log2:
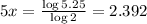
Divide both sides of the equation by 5:
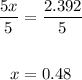
The answer is option A.