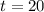Solution:
Given that the number of bacteria in a culture, N, at time t is expressed as
The rate of change is expressed by taking the derivative of the above relation with respect to t.
This gives:
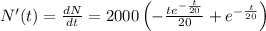
Thus, when the rate of change equals zero, we have
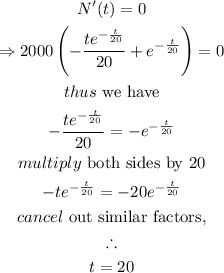
Hence, the rate of change of of the number of bacteria equals zero when