Step-by-step explanation
We can represent the situation in the following picture:
By applying the trig. ratio we can get the angle of the resultant vector as shown as follows:
Assuming that the angle is called α,
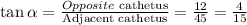
Applying tan^-1 to both sides:
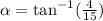
Computing the argument:
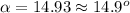
In conclusion, the angle is 14.9 degrees