Answer:
• Yes
,
• c=0
Step-by-step explanation:
Given the function, G(x):
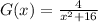
Rolle's Theorem:
According to this theorem if the given function is:
• continuous in [a,b]
,
• differentiable in (a,b)
,
• f(a) = f(b)
then, there exist c in (a,b) such that f'(c)=0.
Continuity of function:
Since the given function is continuous function, it is continuous everywhere. Therefore, G(x) is continuous in [-2,2]
Differentiability
The rational function is differentiable using the quotient rule. Therefore, G(x) is differentiable in (-2,2).
Next, evaluate G(-2) and G(2):
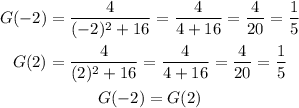
Thus, Rolle's theorem applies on G(x).
Next, we find the possible values of c.
By Rolle's theorem, there exist c in (a,b) such that f'(c) = 0.
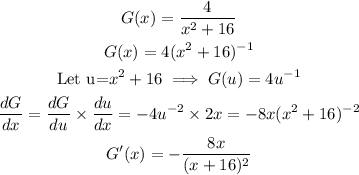
Thus:
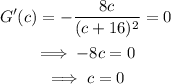
Since c should be in the interval [-2,2], the value of c that satisfies the theorem is 0.