We first have to put the equation in the polynomial's standard form.
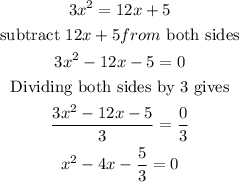
As we now have the equation in the polynomials' standard form, we have a nonfactorizable quadratic equation so we can either employ the completing the square method or formulae method.
We'll use the completing the square. This is simply adding the square of half of the second coefficient to both sides to make the left-hand side factorizable.
![undefined]()