We have a right triangle and two of its sides: one leg and the hypotenuse. In order to find the remaining side we can use the pythagorean theorem. For a right triangle with legs a and b and hypotenuse c we have:
![c=\sqrt[]{a^2+b^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/6uwqakmkjq6nua21bpopztkrf20jt2flji.png)
Using this in our question we get:
![\begin{gathered} 9=\sqrt[]{5^2+x^2} \\ 9=\sqrt[]{25+x^2} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/3zj77wjjp4ewlnxn3sayokml6oze57tful.png)
So the equation to be used to find the missing length is:
![9=\sqrt[]{25+x^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/x4bh8zyf2n85ggrwzdw8fk468ru2przygb.png)
In order to find x we can square both sides of that equation:
![\begin{gathered} 9^2=(\sqrt[]{25+x^2})^2 \\ 81=25+x^2 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/ko0zy1piu3sgruy7iel7um071w9b3qkf8o.png)
Then we substract 25 from both sides:
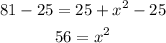
And we apply a square root to both sides:
![\begin{gathered} √(56)=√(x^2) \\ x=\sqrt[]{56} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/dm6ttyb7kyue12e8q2e4mml9pc68v76ffe.png)
And that's the value of x.