First, let's decompose the grasshopper speed V in its horizontal and vertical velocities Vx and Vy:
![\begin{gathered} V_x=V\cdot\cos (45\degree) \\ V_x=V\cdot\frac{\sqrt[]{2}}{2} \\ \\ V_y=V\cdot\sin (45\degree) \\ V_y=V\cdot\frac{\sqrt[]{2}}{2} \\ \\ V_x=V_y=v \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/7ukayyokaobbp1kcrj1uxz5i1az46jd7c2.png)
For the vertical movement, let's use the following formula for the change in speed during the whole movement. The initial vertical speed is v, and the final vertical speed is -v (same magnitude but opposite direction, when the grasshopper reaches the ground). The acceleration is the gravity acceleration (a = -9.8 m/s²).
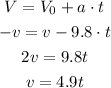
Now, for the horizontal movement, we have:

Calculating the average horizontal speed, we have:

Therefore the average horizontal speed is 1.98 m/s.