Given
The circle graph shows how the annual budget for a company is divided by department.
If the amount budgeted for Media and Engineering combined is $15,000,000,
To find the total annual budget.
Explanation:
Let x be the annual budget.
Since the amount budgeted for Media and Engineering combined is $15,000,000.
Then,
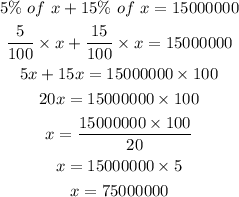
Hence, the annual budget is $75000000.