ANSWER
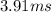
Step-by-step explanation
Parameters given:
Mass of hockey puck, m1 = 0.3 kg
Mass of bottle, m2 = 1.4 kg
Initial velocity of hockey puck, u1 = 17 m/s (taking East as positive direction)
Initial velocity of bottle, u2 = 0 m/s
Final direction of bottle/puck = 40° South of East
To find the resultant velocity of the puck, we have to apply the principle of conservation of momentum, which states that:
This implies that the final momentum must be equal to the initial momentum.
Therefore:
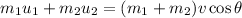
where v represents the final velocity of the puck/bottle and cosθ indicates that the direction of the final velocity is at an angle θ.
Solve for v by substituting the given values:
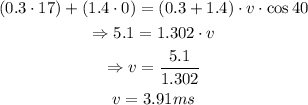
That is the final velocity of the stuck puck.