Answer:
Kinetic energy = 44.1m Joules
where m represents the mass of the ice block
Explanations:
The Kinetic Energy is given by the formula:
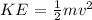
Since the path is frictionless, energy at the initial point equals the energy at point A
The energy at the initial point is:
PE = mgh
h = 4.5 m, g = 9.8 m/s²
PE = m x 9.8 x 4.5
PE = 44.1m
The energy at the point A:
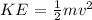
Since PE = KE
![\begin{gathered} 44.1m\text{ = }(1)/(2)mv^2 \\ 88.2m=mv^2 \\ v^2\text{ = }(88.2m)/(m) \\ v\text{ = }\sqrt[]{88.2} \\ v\text{ = }9.4\text{ m/s} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/xb5tpgl7olo82322vc7ahizs8s44bsjlmp.png)
The KE energy will therefore be calculated as:
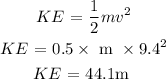
Kinetic energy = 44.1m Joules