The Solution:
Given the logarithmic equation below:
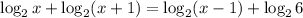
We are required to find the value(s) of x.
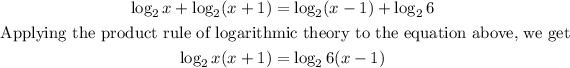
Dividing both sides by log to base 2, we have
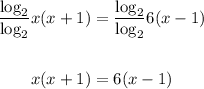
Clearing the brackets, we get
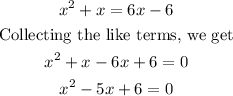
Solving the above quadratic equation using the Factorization Method, we get
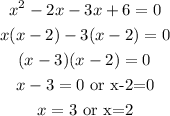
Therefore, the correct answer are: x=3 or x=2