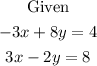
Add each terms from both equations
-3x + 8y = 4
+ (3x - 2y = 8)
0x + 6y = 12
6y = 12
Solve for y, using 6y = 12
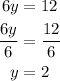
Substitute y = 2, to any of the two equation, in this case, we will use the second equation (using the first equation will yield the same result)
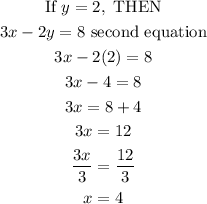
With x = 4, and y =2, the solution in ordered pair form is (4,2).