Given data:
* The mass of the object is m = 6 kg.
* The initial velocity of the object is u = 4m/s.
* The final velocity of the object is v = 3 m/s.
* The force acting on the object is F = 2 N.
Solution:
According to Newton's second law, the force acting on the object in terms of the acceleration of the object is,
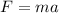
Substituting the known values,
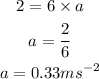
As the acceleration is decreasing the velocity, thus, the value of acceleration is,
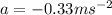
By the kinematics equation, the distance traveled by the object in terms of the acceleration, initial velocity, and final velocity is,
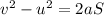
where S is the distance traveled by the object,
Substituting the known values,
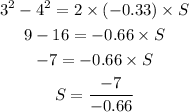
By simplifying,
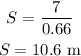
Thus, the distance for which force act to change the velocity from 4 m/s to 3 m/s is 10.6 meters.