Let "x" represent the shorter leg of the triangle.
Then, the long leg is 7m longer than the shorter leg, we can represent this as "x+7"
And the hypothenuse is 9m longer than the shorter leg, we can represent this as "x+9"
The Pythagoras theorem states that the square of the hypothenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the sides of the triangle, so that:
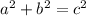
a: shortest leg
b: longest leg
c: hypothenuse
Replace with the expressions for each side:
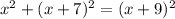
First solve both square of the binomials separatelly from the main expression:
1)
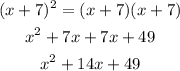
2)
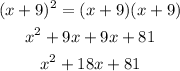
Now that both terms are solved, input the results in the main expression
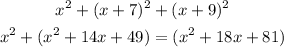
Now we need to equal the expression to zero, so perform the inverse operation to pass all terms to the left side of the equal sign

Order all like terms together and simplify:
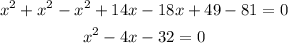
With this, we stablished a quadratic expression. Using the quadratic formula we have to calculate the possible values of x
![x=\frac{-b\pm\sqrt[]{b^2-4ac}}{2a}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/rxvf73usjbbwyik14knxdemoz21vfz2ufc.png)
For our expression
a=1
b=-4
c=-32
Imput these values in the formula and calculate:
![\begin{gathered} x=\frac{-(-4)\pm\sqrt[]{(-4)^2-4\cdot1\cdot(-4)}}{2\cdot1} \\ x=\frac{4\pm\sqrt[]{16+16}}{2} \\ x=\frac{4\pm\sqrt[]{32}}{2} \\ x=\frac{4\pm4\sqrt[]{2}}{2} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/ok6b3vlg7u0n8wetu00vpo364shq158j0h.png)
Now calculate both values of x:
Positive
![\begin{gathered} x=\frac{4+4\sqrt[]{2}}{2} \\ x=2+2\sqrt[]{2} \\ x\cong4.828 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/su0eox6zo3yxzlsp90yot7wvc0e1toq9oa.png)
Negative
![\begin{gathered} x=\frac{4-4\sqrt[]{2}}{2} \\ x=2-2\sqrt[]{2} \\ x\cong-0.828 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/kf67rw0j75bdmnba9g43vc22gx797rr8db.png)
The length of the side of a triangle cannot be a negative value, so the only possible value of x will be:
![x=2+2\sqrt[]{2}=4.828m](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/d63ujyogg4b3mkotc3u88plz583kuo6ugz.png)
Now that we know the value of the shortest leg, we can calculate the value of the longest leg and the hypothenuse:
Longest leg
![x+7=(2+2\sqrt[]{2})+7=9+2\sqrt[]{2}\cong11.828m](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/64k73miegf82sxopmmpu44nbgoo8s22165.png)
Hypothenuse
![x+9=(2+2\sqrt[]{2})+9=11+2\sqrt[]{2}\cong13.828m](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/ozo0sl2vy8a9wp5rwxv1u1xsvodbht6co5.png)