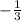Answer
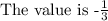
Given
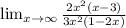
Solution
Let take the common factor first
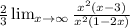
Let's apply algebraic property:
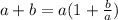
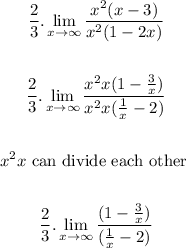
Let take the limit of the numerator
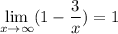
Also take the limit of the denominator
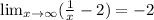
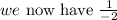
Now, let not forget the common factor outside
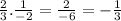
So therefore, the Limit exist and the value is