Step 1: Find (x² + 1)²
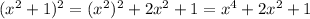
Step 2: Find (x² - 1)²
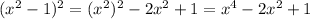
Step 3: Find the sum of (x² - 1)² + (2x)²
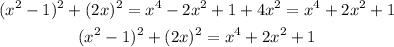
Comparing the final result in step 1 with the final result in step 2
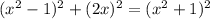
Hence, the sum of the squares of the two shorter sides is equal to the square of the longer side
This is a property of right angled triangle
Hence