Givens.
• R = 30 cm.
,
• t = 4 seconds.
,
• a_n = 2.7 m/s^2.
,
• n = 3 revolutions.
First, we need to find the angular acceleration.
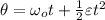
But, we need to find the angular displacement and the angular speed.
![\begin{gathered} \theta=3rev\cdot(2\pi)/(1rev)\cdot=6\pi \\ a_n=(v^2)/(R)\to v^2=a_n\cdot R=v=\sqrt[]{2.7\cdot(m)/(s^2)\cdot0.30m} \\ v=0.9\cdot(m)/(s) \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/50xuz6hfuwgdusurp32pz748ji1m66uzdp.png)
The displacement of 3 revolutions is 6pi radians and the tangential (linear) speed of 0.9 m/s. Use the radius to find the angular speed.
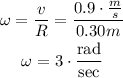
Once we have the angular speed and the angular displacement, we are able to find the angular acceleration.
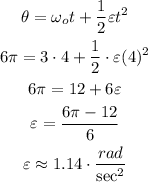
Once we have the angular acceleration, we can find the tangential acceleration.
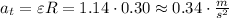
The tangential acceleration is 0.34 m/s^2.
The total acceleration would be
![\begin{gathered} a_{\text{total}}=\sqrt[]{a^2_t+a^2_n}=\sqrt[]{(0.34)^2+(2.7)^2} \\ a_{\text{total}}=\sqrt[]{0.1156+7.29}\approx2.72\cdot(m)/(s^2) \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/2427s6rdjgg306b9c3y5q7u055spx32z3l.png)
The total acceleration is 2.72 m/s^2.
The linear velocity is 0.9 m/s.
The angular velocity is 3 rad/sec.