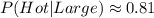Conditional probability:
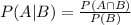
The probability that A occurs given that B has occurred is given in the formula above.
As in our problem we are asked for the probability that a customer ordered a hot drink (event A) given that he or she ordered a large (event B), then we can work with the formula.
• The union between hot drink and large can be written as follows, and this is equal to 22 as we can see in the table.
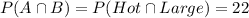
• The probability of a large (event B) is the addition of all the possibilities of ordering large:
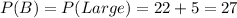
Finally, we replace these values in the formula:
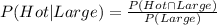
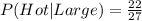
Answer: