a) x = 6, y = 0
Ordered pair: (6, 0)
x = 0, y = 2
Ordered pair: (0, 2)
b) x = -5, y = 0
Ordered pair: (-5, 0)
x = 0, y = 3
Ordered pair: (0, 3)
Step-by-step explanation:
a) 2x + 6y = 12
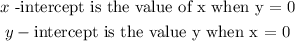
To get x-intercept, we substitute 0 for y:
2x + 6(0) = 12
2x + 0 = 12
2x = 12
x = 12/2
x = 6
x = 6, y = 0
Ordered pair: (6, 0)
To get y-intercept, we substitute 0 for x:
2(0) + 6y = 12
0 + 6y = 12
6y = 12
y = 12/6
y = 2
x = 0, y = 2
Ordered pair: (0, 2)
b) 3x - 5y = -15
x-intercept: y = 0
3x - 5(0) = -15
3x - 0 = -15
3x = -15
x = -15/3
x = -5
x = -5, y = 0
Ordered pair: (-5, 0)
y-intercept: x = 0
3(0) - 5y = -15
0 - 5y = -15
-5y = -15
y = -15/-5
y = 3
x = 0, y = 3
Ordered pair: (0, 3)