SOLUTION
Given the question in the question tab, the following are the solution steps to find the amount of flooring needed to cover the room
Step 1: Write out the given measurements
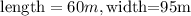
Step 2: Calculate the area of the room, this will be the amount of flooring needed to cover the room.
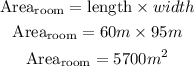
Hence, the amount of flooring needed to cover the room is 5700 square meters.