First, we need to calculate the amount of time that the balls are falling, using the formula:
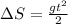
Where DeltaS is the distance traveled, g is the gravity acceleration and t is the time.
So, for DeltaS = 125 and g = 10, we have:
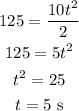
Now, to find the initial speed v, we can use the formula for the distance traveled in the horizontal movement:
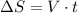
For DeltaS = 30 and t = 5, we have:
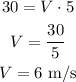
So the initial speed v is 6 m/s.