This is an arithmetic sequence since we have that:
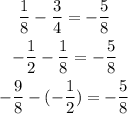
and then we have a common difference between each term of -5/8.
The nth term of an arithmetic sequence can be express as:
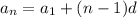
in this case the fisrt tems is 3/4 and the common difference, d, is -5/8; hence the nth term can be express as:
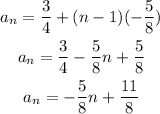
Hence the nth term is given by:
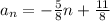
To determine if the sequence converge or diverge we need to determine its behaviour for large n, that is we need to calculate the limit:
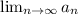
since the sequence is linear in n this means that this limit will diverge; therefore the sequence is divergent.
Now that we know that the sequence diverges we need to remember that if the limit of the sequence does not have a finite value hence the series diverges as well. Hence the series is divergent.
With this in mind we conclude that both sequence and series are divergent and therefore the answer is D.