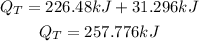Answer:
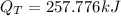
Step-by-step explanation:
The total heat energy required is expressed according to the formula:
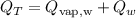
where:
Qvap is the heat energy absorbed by the vapor
Qw is the heat energy absorbed by the water
Get the heat energy absorbed by the vapor at 100 degrees
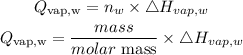
Given the following parameters;
Mass of water = 100g
Molar mass of water (H2O) = 18.015g/mol
Hvap,w = 2259 J/g = 40.8 kJ/mol
Substitute the given parameters into the formula to have:
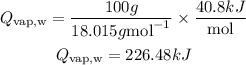
Get the heat absorbed by the water from 30 to 100 degrees and from 100 to 110 degrees using the formula below. Note that the water vapor is being heated without any phase changes, so we will be utilizing the specific heat capacity of water vapor.
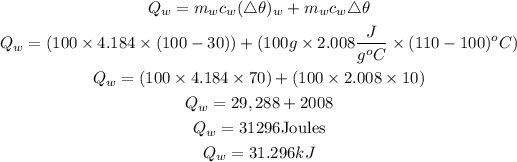
Get the total heat energy required;