When we are solving an equation and we get an equivalent one that says 0=0, this means that the equation we are solving will be satisfied by any real number defined in the domain of the expression defining the equation.
Example.
Suppose we have the equation:
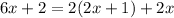
if we try to solve it we have:
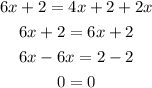
This means that no matter the value of x, the equation holds.
Assume that x=1, then:
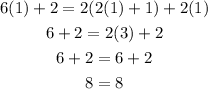
then, for x=1 the equation holds.
Now, assume that x=-5, then:
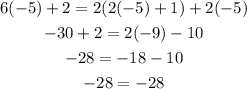
then, for x=-5 the equation holds.
We can keep doing this with all the numbers and the equation will always be satisfied.