We know that the exterior angle theorem states that the measure of each exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the opposite and non-adjacent interior angles. In this case this means that:
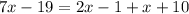
Solving for x we have:
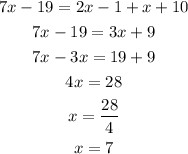
Once we know the value of x we pluf it in the expression for the angle we want:
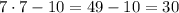
Therefore, the angle CDE is 30°.