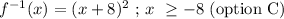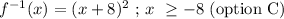
Step-by-step explanation:
![f(x)\text{ = }\sqrt[]{x}\text{ - 8}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/lt4jb24rhmdz0hg8e2mcc6udvbx20usecy.png)
let y = f(x)
![y\text{ = }\sqrt[]{x}\text{ - 8}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/i8hpah8s2fswb6dv1la8ljg7bg9bc8d3p4.png)
To get the inverse of f(x): first, we will interchange y and x. Then we will solve for y.
![\begin{gathered} In\text{tercahnge y and x:} \\ x\text{ = }\sqrt[]{y}\text{ - 8} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/61z8qodzq67dmxm8zgl5wlm2f23a0z3yez.png)
Add 8 to both sides:
![\begin{gathered} x\text{ + 8 = }\sqrt[]{y}\text{ - 8 + 8} \\ x\text{ + 8 = = }\sqrt[]{y} \\ \text{square both sides:} \\ (x+8)^2\text{ = (}\sqrt[]{y})^2 \\ y\text{ = }(x+8)^2\text{ } \\ \\ \text{Hence, }f^(-1)(x)\text{ = }(x+8)^2\text{ } \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/jjrl8m5e9yrclndjtzpx50kmmm9pzjlj5z.png)
Domain are the inputs of a function. They are the x values.
The inverse of f(x) doesn't have a denominator.
The domain of an inverse functon is the range of the original function
Range (y values ) of original function was x ≥ -8
Hence, domain of this function is x ≥ -8