Answer
For part A: The final pressure of the helium gas = 292.2 mmHg
For part B: The final pressure of the helium gas = 1920 mmHg.
Step-by-step explanation
Part A:
The final pressure, in mmHg of the helium gas, can be calculated using Boyle's law formula:
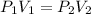
Putting
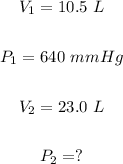
We have:
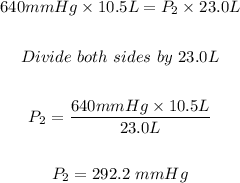
For part A: The final pressure of the helium gas is 292.2 mmHg.
Part B:
Similarly, the final pressure, in mmHg of the helium gas, can be calculated using Boyle's law formula:
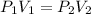
Putting
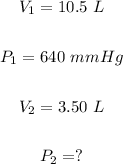
We have:
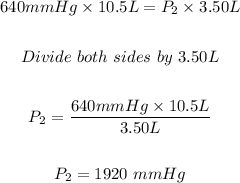
For part B: The final pressure of the helium gas is 1920 mmHg.