One whole unit circle has an angle of 2π. So, if our angle is 5π, this would be two revolutions and a half. This means that the terminal ray of this angle lies in Quadrant II at the x-axis.
The angle has an x-value of -1, a y-value of 0, and an r-value of 1.
So, the value of the six trigonometric functions are:
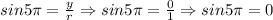
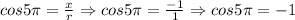
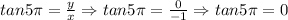
![csc5\pi=(r)/(y)\Rightarrow csc5\pi=(1)/(0)\Rightarrow csc5\pi=undefined]()
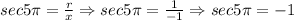
![cot5\pi=(x)/(y)\Rightarrow cot5\pi=(-1)/(0)\Rightarrow cot5\pi=undefined]()