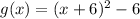Step-by-step explanation
We can use the following rules of transformation of functions:
• f(x - h) moves the function h units right.
• f(x + h) moves the function h units left.
• f(x) + k moves the function k units up.
• f(x) - k moves the function k units down.
From the graph of h(x), we can determine the parent function and then transform it to obtain the graph of g(x).
Analyzing the graph of h(x), we have:
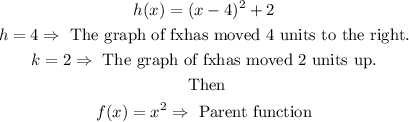
Now, we can obtain the graph of g(x):
![\begin{gathered} f(x)=x^2\operatorname{\Rightarrow}\text{Parent function} \\ h=6\Rightarrow\text{ The graph of f\lparen x\rparen has moved 6 units to the left.} \\ k=6\Rightarrow\text{ The graph of f\lparen x\rparen has moved 6 units down.} \\ \text{ Then} \\ g(x)=(x+6)^2-6 \end{gathered}]()
Answer