In a right triangle, we can use the pythagorean theorem to find the side lengths.
Algebraically, pythagorean theorem is:
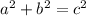
Alternately, it is:
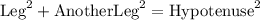
Given,
Hypotenuse = 15
Leg = 10
Let's find QP:
![\begin{gathered} 10^2+\text{AnotherLeg}^2=15^2 \\ 100+QP^2=225 \\ QP^2=225-100 \\ QP^2=125 \\ QP=\sqrt[]{125} \\ QP=\sqrt[]{25*5} \\ QP=\sqrt[]{25}*\sqrt[]{5} \\ QP=5\sqrt[]{5} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/oxpzpbqn0jj3c32r82okl10o5v3u1anj7a.png)
With respect to Angle R, we can write:
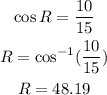
We know 3 angles in a triangle add to 180 degrees. So, we can write:
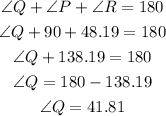
The answers are:
![\begin{gathered} QP=5\sqrt[]{5}=11.18\text{ cm} \\ \angle R=48\degree \\ \angle Q=42\degree \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/ngoiycgn1y74sbgkgp0z4fgf3m1nlo2ffd.png)