ANSWER
This is an isosceles right triangle
Step-by-step explanation
If we calculate the distance between vertices (-1, -4) and (-4,0):
![\begin{gathered} d=\sqrt[]{(-1-(-4))^2+(-4+0)^2} \\ d=\sqrt[]{3^2+4^2} \\ d=\sqrt[]{9+16} \\ d=\sqrt[]{25} \\ d=5 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/v5l61kow2twcwrtzglphxj5tfdsr5aas47.png)
And between vertices (-4,0) and (0, 3):
![\begin{gathered} d=\sqrt[]{(-4+0)^2+(0-3)^2} \\ d=\sqrt[]{4^2+3^2} \\ d=\sqrt[]{16+9} \\ d=\sqrt[]{25} \\ d=5 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/rdh0f9kbpr28cxsimmk2nhb4mednqzw65i.png)
We have the same distance. Therefore this two sides are congruent. The distance between vertices (0, 3) and (-1, -4) is:
![\begin{gathered} d=\sqrt[]{(0-(-1))^2+(3-(-4))^2} \\ d=\sqrt[]{1^2+7^2} \\ d=\sqrt[]{50} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/pidjq5mqxre2uvhtsywwsdas46jts4dqpw.png)
It's different from the other two sides, so this is an isosceles triangle.
Also, if the sides meet the Pythagorean theorem the triangle is a right triangle:
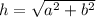
h is the hypotenuse and a and b are the sides. If the sides are the congruent sides and the third side (the longest) is the hypotenuse we have:
![\begin{gathered} \sqrt[]{50}=\sqrt[]{5^2+5^2} \\ \sqrt[]{50}=\sqrt[]{25+25} \\ \sqrt[]{50}=\sqrt[]{50} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/42fpmjt5q60tsyic7cgznxzc4ca154of6z.png)
This isosceles triangle is also a right triangle