vertex for function 1 : (-2,4)
vertex for function 2: (2,7)
function 1 has the smaller value
it is 4
Step-by-step explanationgiven
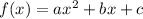
to get the vertex from the quadratic function we need to use
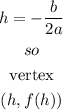
then
Let
Step 1
Function 2
Let
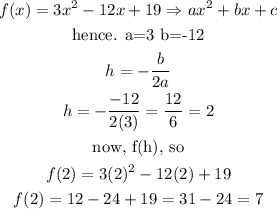
hence, the vertex is
vertex: (2,7)
Step 2
function 1
we have the table, so
a) find the function
so
for x= 1
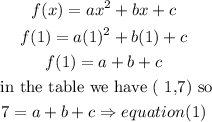
for x= -2
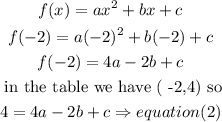
for x= 4
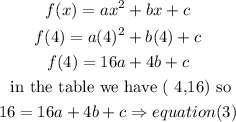
now, we have a system of 3 variables and 3 equations, so
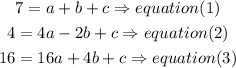
a) subtract equation (2) from equation (1) to eliminate c
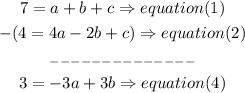
b) subtract eq(3) from eq(1) to eliminate c
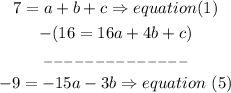
c) now, add equation (4) and equation(5) to eliminate b
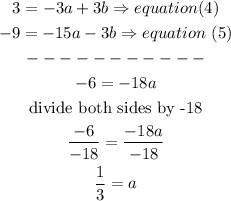
now, replace in equation (4) to find b
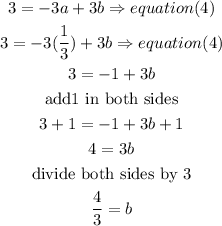
d) finally, replace a and b values into equation (1) , then solve for c
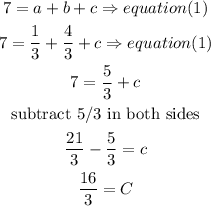
hence, the function is
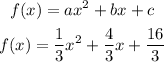
now, apply the formula to find the vertex
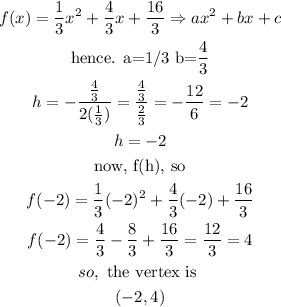
vertex for function 1 : (-2,4)
Step 3
smaller minimum value:
let's compare the image of the vertex
vertex for function 1 : (-2,4)
vertex for function 2: (2,7)
the y coordinate the function 2 is greater, so
function 1 has the smaller value
it is 4
I hope this helps you