Given,
The mass of the student, M=45.5 kg
The mass of the skateboard, m=4.5 kg
The initial velocity of the skateboard, u=0 m/s
The final velocity of the student and the skateboard, V=4.8 m/s
From the law of conservation of momentum, the total momentum of the student and the skateboard before the student jumps on the skateboard must be equal to the total momentum of the student and the skateboard after the student jumps on it.
Thus,
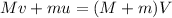
Where v is the initial velocity of the student.
On rearranging the above equation,
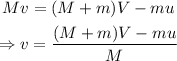
On substituting the known values,
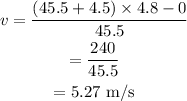
Thus the initial velocity of the student must be 5.27 m/s