The Pythagorean theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of squares of the other 2 legs in a triangle.
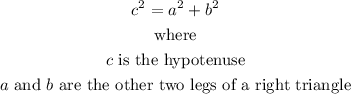
In the given figure, we have side lengths 3 and 4, with the value of the hypotenuse missing.
Substitute the following values to get the missing length of the hypotenuse
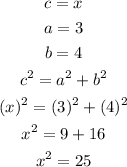
Get the square root of both sides to get the value of the hypotenuse
![\begin{gathered} \sqrt[]{x^2}=\sqrt[]{25} \\ x=5 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/c736ivxli0lc0p6qy6lrg2g1xnnbljlp3j.png)
Therefore, the missing side length x is equal to 5 units.