Given:
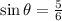
Required- the values of cos θ and tan θ.
Step-by-step explanation:
We know that in a right-angled triangle, for any angle θ, the value of sin θ, cos θ, and tan θ is:
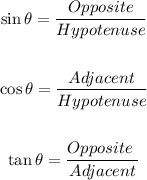
From the given value of sin θ, we get:
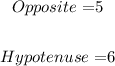
Now, we calculate the value of Adjacent by the Pythagoras theorem as:
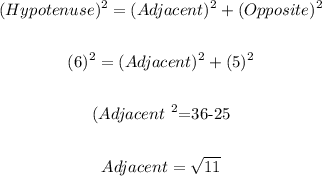
Now, the value of cos θ is:
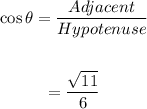
Now, the value of tan θ is:

Final answer: The value of cos θ and tan θ is √11/6 and 5/√11 respectively.