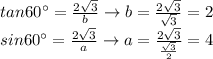Answer:
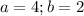
Explanation:
1. The unmarked angle is 30° (since unmarked, +60°, a right angle will add to 180°)
2. Mirror the triangle over the known side. The triangle you get is an equilateral triangle. This allows us to say 2b = a
At this point, pythagorean theorem:
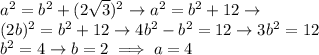
Only the positive solution is taken since it's a length of a segment.
Same result can be obtained with trigonometry if you are allowed to use higher grade math. In particular