6.1)
The denominator is a difference of squares. It can be factored as a product of conjugate binomials:
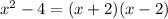
On the numerator, the coefficient of x^2 is 3 and the constant term is 4. The product of 3 and 4 is 12, and the factors of 12 which sum to 8 are 2 and 6.
Rewrite 8x as 2x+6x, then factor the resulting polynomial:
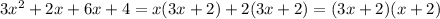
Then, the function can be written as:
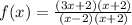
6.2)
Since the factor (x+2) appears both in the numerator and in the denominator of the function, then the function will have a hole when x+2 equals 0.
Set x+2 equal to 0 and isolate x to find the x-value of the hole:
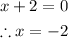
6.4)
The end behavior of the function can be found as the quotient between the coefficients of the leading terms of the numerator and the denominator when both have the same degree.
In this case, both the numerator and the denominator are 2nd degree polynomials.
The coefficient of the leading term of the numerator is 3 and the coefficient of the leading term of the denominator is 1.
Then, as x approaches plus or minus infinity, the function f(x) will approach 3/1, which is equal to 3.