We know that the final velocity of the object is 18 m/s in a direction of 47° from the x-axis; this means that the final velocity as vector is:
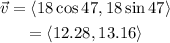
Now, since the acceleration is along the x-axis this means the the y-component of the initial velocity remains constant; hence the y-component of the final velocity is the same as the y-component of the initial velocity. This also means that the x-component is the only one that changes; since the acceleration is constant throught the 2.7 seconds we can use the formula:
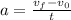
To find the x-component of the initial velocity:
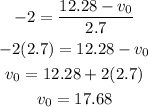
Therefore the initial velocity is:
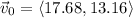
Its magnitude is:
![\begin{gathered} v_0=\sqrt[]{(17.68)^2+(13.16)^2} \\ v_0=22.04 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/high-school/glcgb4jos1nta7iaahl92f80zs80az5mfe.png)
Therefore the magnitude of the initial velocity is 22.04 m/s.