The probability of picking a sample that is from group B, and type Rh+ is
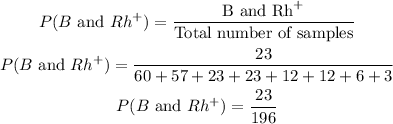
Part A:
Given that the selection are made with replacement, the probability that the 2 selected subjects are both group B and type Rh+ is

Rounding our answer to four decimal place, the probability is 0.0138.
Part B:
If without replacement is made within the selection, the probability is changed so that
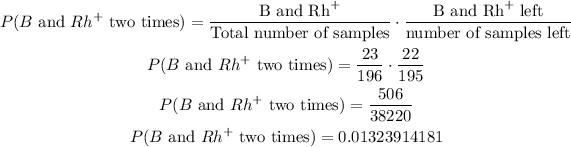
Rounding to answer to four decimal place, the probability is 0.0132