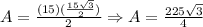We will have the following:
a. We can see that the angle opposite to x is 45° and the angle opposite to 10 is also 45°; from theorems [Congruent angles that oppose sides in a triangle have that those sides are also congruent]; so:
x = 10.
Now, we determine y using the law of sines:
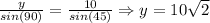
Now, we determine the height of the triangle:
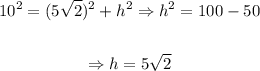
So, the perimeter is:
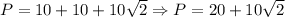
The area is:
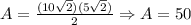
b. Same as in the previous triangle we will determine x and y:
x = 15
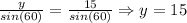
Now, we determine the height of the triangle:
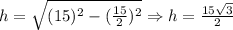
So, the perimeter is:
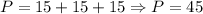
The area is: