Rico already has 350.00 from his savings and the amount his ninong gave him; this means that he only needs to save:
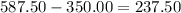
more.
Let x be the number of days he is going to save, since he saves 12.50 each day then for x days he will have 12.5x, we need this to be equal to 237.50 then we have the equation:
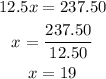
Therefore he needs to save for 19 days.