To find:
The sketch of v, 2v and 1/2 v.
Solution:
Given the v = <3,2>.
(a)
The sketch of v is shown below:
(b)
The value of 2v can be obtained as follows:
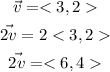
The sketch of 2v is shown below:
(c)
The value of 1/2 v can be obtained as follows:
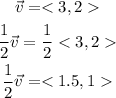
The sketch of 1/2 v is shown below: