Given the functions:
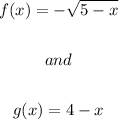
Let's find the domain of (g - f)(x) in interval notation.
To solve for (g - f)(x), let's solve for g(x) - f(x).
Subtract f(x) from g(x).
We have:
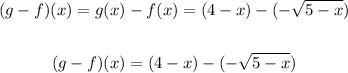
Solving further:
Apply distributive property and remove the parentheses.
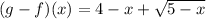
Now, let's find the domain.
The domain is the set of possible values of x which makes the function defined.
To find the domain set the values in the radicand greater or equal to zero and solve for x.
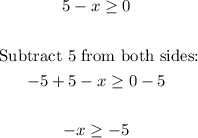
Divide both sides by -1:
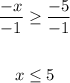
Therefore, the domain is:
x ≤ 5
In interval notation, the domain is:
![(-\infty,5]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/o7eqtm613lysu49ieqjg1uob38h8o89i37.png)
ANSWER:
![(-\infty,5]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/o7eqtm613lysu49ieqjg1uob38h8o89i37.png)